The ATX motherboard processor sockets used by AMD and Intel CPUs
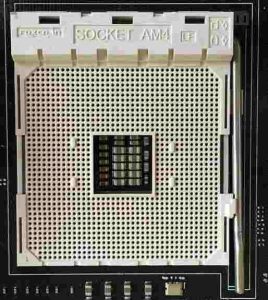
Desktop PC CPU / processor sockets
This page of this website is devoted purely to the many different types of desktop PC processor sockets used by Intel and AMD processors on ATX motherboards specifically for one or more ranges of their processors.
Will Windows 11 run on your current Win10 computer?
Note that only certain AMD and Intel processors have Microsoft’s support for Windows 10 to upgrade to Windows 11 .
Windows 11 supported Intel processors –
Windows 11 supported AMD processors –
The following article provides the information on all of the support requirements and other information.
Will Windows 11 run on your current Win10 computer? –
https://www.pcbuyerbeware.co.uk/blog/will-windows-11-run-on-your-current-win10-computer/
There are several free tools that identify the make/model of CPU in use on a desktop or laptop PC. I use HWINFO64, shown below.
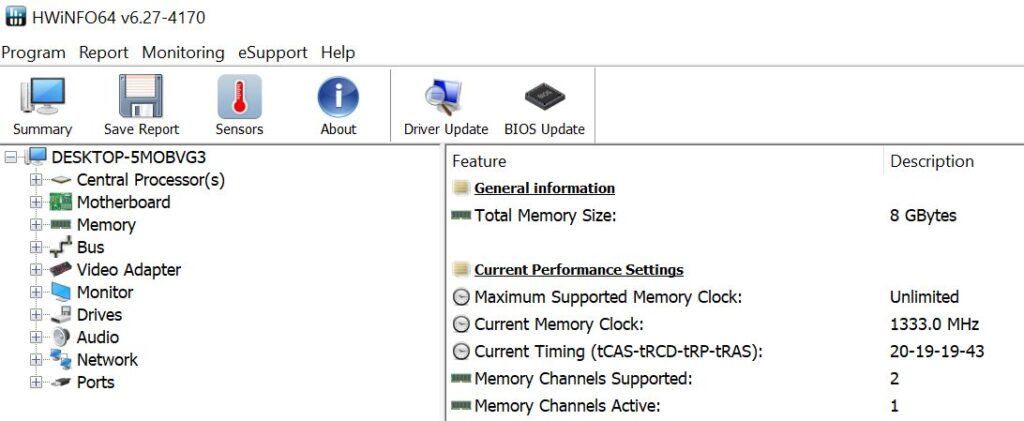
Other tools that provide that information are CPU-Z and the Belarc Advisor. Of course, you can identify the make/model of CPU by opening the case and removing the cooling unit and any thermal past on the CPU that is covering that information (shown below).

For detailed information on desktop processors, visit the The Intel and AMD processors used in desktop PCs section of this website.
For information on installing a processor, visit the Installing the processor (CPU) and its heatsink-and-fan or liquid-cooling unit page of the Build Your own PC section of this website.
The pace at which the socket types have been changing has slowed down considerably since the heyday of the desktop PC, which is in decline compared to tablet PCs and smartphones, now enjoying their heyday.
Personally, I don’t see desktop and laptop PCs becoming redundant any time soon. I would much rather have a laptop PC than any tablet and I use a desktop PC at home. Laptops are still relatively expensive. If I want to upgrade my desktop PC to the latest hardware, I just have to back up my files and go online and buy a motherboard, processor and RAM bundle costing about £150. Then it’s just a question of reinstalling Windows, my software and restoring my files. Microsoft’s ISO download of Windows 10 is always right up to date. Gone are the days when you had to create a ‘slipstreamed’ install disc that added Service Packs to an earlier Windows install disc.
The following post deals with how to obtain the Windows 7/8.1/10 downloads to create an installation disk.
Where to get an ISO image used to create a Windows 10, 8.1 and 7 installation DVD or flash drive –
https://www.pcbuyerbeware.co.uk/blog/use-windows-10-8-7-iso-image-create-install-dvd-flash-drive/
Processor-related posts on this website
POST: The amazing AMD Ryzen 5000 series desktop-PC processors are available now
POST: How to decode Intel/AMD processor names – What processor names mean
POST: Intel vs AMD processors – 8th generation Intel Core Coffee Lake vs AMD Ryzen processors (CPUs)
POST: AMD Ryzen 3, 5 and 7 processors (CPUs) strike back hard at Intel dominance
How to decode Intel/AMD processor names – What processor names mean
The alphanumeric model names of the ranges of processors that Intel and AMD manufacture contain important information about them. The following article provides the information you need to understand what the numbers and letters in the model number mean.
https://www.pcbuyerbeware.co.uk/blog/meaning-intel-amd-processor-names/
How to tell if AMD and Intel processors come with built-in graphics chips or not
Graphics cards are in short supply due to Covid-19 lockdowns. Consequently, you will probably find buying a separate graphics card difficult. Intel and AMD processors can come with a built-in graphics chip (GPU). If you want to rely on the graphics that a processor’s graphics chip provides, you need to know how to tell from the Intel and AMD processor’s model name which models come with one.
Most current Intel processors come with a built-n graphics chip. If the processor does NOT come with one, its model name has the letter F as the last letter in the name.- An example is the Intel Core i9-10900F, which does not provide a graphics chip.
AMD uses the opposite method. With AMD Ryzen processors, the model must have the letter G (that stands for Graphics) as the last letter in its model name if it has a built-in graphics chip. The letter at the end of the model name indicates that it has a graphics chip. Most AMD Ryzen processors do not have the letter G in their model name and so do not have a built-in graphics chip. An example is the third-generation AMD Ryzen 5 3400G that provides a graphics chip.
Comprehensive list of AMD Ryzen processors –
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_AMD_Ryzen_processors
Processor information and installation
The following pages provide information about processor themselves and how to install them:
Intel and AMD Processors (CPUs) Used in Desktop PCs –
https://www.pcbuyerbeware.co.uk/hardware/processors/
Installing the processor (CPU) and its heatsink-and-fan or liquid-cooling unit –
https://www.pcbuyerbeware.co.uk/hardware/build-your-own-pc/12/
Annotated images of ATX Socket Intel LGA 775, AMD Socket A and Socket 939 motherboards
Visit the Annotated images of ATX Socket LGA775, Socket A and Socket 939 motherboards page on this website to see annotated images of those two socket-type motherboards.
AMD and Intel motherboard processor sockets are never interchangeable
Although they can be very different electronically, CPU sockets all look similar at first glance, being square and about the same size no matter how many processing cores the processor itself contains – processors get thicker as their core number increases – and can be seen immediately when examining a PC’s motherboard.
AMD and Intel motherboard sockets are never interchangeable; they can only be used by the products of the motherboard manufacturers that they have been designed to support.
The rate at which Intel and AMD were changing the type of motherboard sockets that their desktop PC processors use was confusing as well as being infuriating. It meant that even if the motherboard form-factor remained the same (ATX or micro-ATX), every time the type of processor housing changed or there were technical changes to the existing platforms, if Intel was your choice of manufacturer, a new motherboard usually had to be purchased if you wanted to upgrade from one type of socket to another. Or having to that was necessary for a more advanced processor that used the same socket type. You had no choice in the matter because the previous processor housing was then no longer supported.
AMD provided far better backward-compatibility of its latest processors with its previous socket type, but, even with AMD, when a radically new CPU architecture came into being a new motherboard was required.
But now that the market for desktop PCs has slowed down considerably since smartphones and tablets became the most popular form of PC, the rate of change of CPU sockets has also slowed down considerably. Computer users are still using their desktop and laptop PCs but are making them last much longer than was the case when the PC was unrivalled.
There was a large increase in PC sales when support for Windows XP ended in June 2014, so, as Windows 7 gets older and more PC users are forced to upgrade to Windows 10 or buy new PCs, there will probably be another similar increase in PC sales that will spark off further technological developments. That said, the dominance that the desktop PC enjoyed has gone forever.
The image at the top of this page shows a zero-insertion-force (ZIF) processor socket. The pin holes match the pin layout of the processor and so, when aligned correctly, the processors that the socket supports should just drop into the socket without using any force.
The processor is dropped into the socket with the brown arm at the bottom of the socket raised. When the processor is inserted, the arm is lowered all the way down, thereby fixing the processor into the socket. AMD has always used pins on its processors. Intel used to use pins but then changed to using metal contact points on the processor that match metal pits in the socket. The heatsink and fan cooling unit is fixed to the plastic protrusions in the middle of the left and right sides of the socket shown in the image above.
All of the specifications of AMD and Intel processors for the desktop PC
Visit the following page that provides access to tables containing all of the technical specifications (socket type, code name (Haswell, Ivybridge, Skylark, etc.) clock speed, supported instruction sets, caches, etc.) and other information, such as the dates of release, of all of the processors made by AMD and Intel up to the present. The earliest processors are listed first. The further down the list a processor appears, the more recent it is. Look down the Socket/Slot column for the socket type for a particular model of processor.
Note that the new AMD Ryzen Threadripper models use the new rectangular Socket TR4. There are three Threadripper models – 8, 12 and 16 cores. The processor, shown held by hand in the image below, is enormous, requiring an enormous socket. Below that image, the Socket TR4 itself is shown in an image of an ASUS PRIME X399-A motherboard (£280 in December 2017). This is AMD’s first LGA (Land Grid Array) socket that has the pins in the socket instead of on the processor, which is called Pin Grid Array (PGA). All of Intel’s processors have been LGA for over a decade, starting in 2004. The Threadripper CPUs only have metal contact points on the bottom of the processor (LGA). The other Ryzen CPUs still use pins on the processor (PGA).


AMD Ryzen 3, 5 and 7 processors (CPUs) strike back hard at Intel dominance –
By January 2021, the Ryzen 3, 5 and 7 5000 series of CPUS were just becoming available, but were in short supply . Examples of the 5000 series are: AMD Ryzen 5 5600X, Ryzen 7 5800X, and the Ryzen 9 5950X. The first number in the long code – 5 in this case – indicates the fifth generation.
POST: The amazing AMD Ryzen 5000 series desktop-PC processors are available now
AMD Ryzen 3, 5 & 7 processors (CPUs) –
https://www.pcbuyerbeware.co.uk/blog/amd-ryzen-3-5-7-processors/
Here are the two pages on Wikipedia that list all of the AMD and Intel processors, including laptop processors, and their specifications, which includes the socket type:
List of AMD microprocessors –
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_AMD_microprocessors
AMD Zen (microarchitecture) – Socket AM4 Ryzen processors –
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zen_(microarchitecture)
List of Intel microprocessors –
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_Intel_microprocessors
Desktop PC Intel and AMD CPU socket types from 2008 to 2021
AMD CPU sockets
List of AMD processors – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_AMD_microprocessors
Socket AM3 – 2009 to 2011 – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Socket_AM3
Socket AM3+ – 2012 – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Socket_AM3%2B
Socket FM1 – 2011 – First socket for the AMD APU CPUs with inbuilt graphics chip –
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Socket_FM1
Socket FM2 – 2012 to 2013 – Second socket for the AMD APU CPUs with inbuilt graphics chip –
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Socket_FM2
Socket AM1 – 2014 – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Socket_AM1
Socket FM2+ – 2014 to 2015 – Third socket for the AMD APU CPUs with inbuilt graphics chip –
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Socket_FM2%2B
Note that Socket FM2+ APUs are not compatible with Socket FM2 motherboards.
Socket AM4 – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Socket_AM4 [AMD Ryzen CPUs up to the 5000 series (2020) and for the latest AMD APUs]
Socket TR4 for the AMD Ryzen Threadripper CPUs – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Socket_TR4
Intel CPU sockets
List of Intel processors – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_Intel_microprocessors
LGA 775 – 2004 to 2008 – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LGA_775
LGA 1156 – 2010 – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LGA_1156
LGA 1366 – 2008 to 2011 – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LGA_1366
LGA 1155 – 2011 to 2012 – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LGA_1155
LGA 2011 – 2011 to 2014 – Versions 2011-1 to 2011-3 – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LGA_2011
LGA 1150 – 2015 – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LGA_1150
LGA 1151 – 2015 – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LGA_1151
LGA 1200 – 2020 – Comet Lake (2020) and Rocket Lake (2021) CPUs –
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LGA_1200
LGA 2066 – 2017 – LGA 2066, also called Socket R4, is a CPU socket by Intel that debuted with Skylake-X and Kaby Lake-X processors in June 2017.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LGA_2066
LGA 1700 – 2021 DDR5 – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LGA_1700
Noctua NH-U12S [CPU cooler] has been secretly changed [for Socket LGA 1700] and it’s NOT GOOD –