Network diagnostics and troubleshooting
Networking and Internet problems
Networking and Internet Problems are dealt with in a separate section of this website.
Diagnostic charts
As you can see from looking at any of the diagnostic charts made available from the following link, there are no photo-illustrations or explanations of basic computer functions, such as accessing the Windows Device Manager. The intended audience is the hobbyist or technician who already has some experience of using and/or repairing computers.
If you can understand a particular flowchart, it would be a good idea to print them just in case you can’t boot your computer and you need the information.
Network Troubleshooting: http://www.fonerbooks.com/network.htm
How to get your modem router line stats [UK routers provided by BT, Plusnet, Belkin, Netgear, Linksys, etc.] –
“When looking at your line stats you can’t just rely on one particular aspect and you have to look at all of the figures to get an overall picture of how your line is performing.” – http://www.kitz.co.uk/adsl/frogstats.php
Connecting devices to a modem-router-based network
Connecting devices to a modem-router-based network is just a matter of connecting the router to the landline telephone connection and computers and other devices to the router by Ethernet cable or by Wi-Fi. Most people use modem routers supplied by their Internet Service Provider (ISP), which provides a user manual. Both cabled and Wi-Fi connections are created automatically using the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) that assigns each computer or network device, including the router, wireless printer, etc.,an internal identifier called an IP Address, which takes this form: 192.168.1.254.
Note that you don’t have to use the router that your Internet Service Provider (ISP) provides. There are many makes/models of router available that you can use if your ISP supports them.
Before investing in a new router, check whether it will work with your internet connection. An ADSL connection requires a router with a built-in ADSL2+. A fibre broadband connection requires a router with VDSL2 support. Some routers, such as the DrayTek Vigor 2860AC model, support both ADSL and VDSLconnections. A feature that would make switching from an ADSL to to a fibre connection easy if the ISP supports the router.
The following article provides useful information on the alternative routers on the market in the UK.
Best wireless routers 2019: Boost the range and speed of your internet connection –
https://www.expertreviews.co.uk/node/1403819
Assigning devices on a Windows home network static (fixed) IP addresses instead of allowing DHCP to assign them automatically often solves connection problems. Each networked device connected by Ethernet cable or by Wi-Fi must be assigned a unique IP address.
IP address – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IP_address
Every time a device starts up, it requests and is assigned an IP Address automatically by the DHCP protocol, because Windows is set to assign IP addresses automatically by default.
The person administering the network can assign each device, connecting to the network by Ethernet or Wi-Fi, a fixed (static) IP address.
Doing that makes network troubleshooting far easier. For example, say that 192.168.1.254 is the fixed IP Address assigned to the router. Any other device can be given an IP Address in the same range below the end number of 254. The router uses the end number 254, the highest possible number in any range, so I would use any end number under it to assign an IP Address to a device, such as 192.168.1.1, 192.168.1.2, etc., up to 253. Every computer connected to the network must have a unique IP Address. If any devices on a network are using the same IP Address, they can’t be individually identified.
The following webpage provides a good tutorial on how to turn off DHCP and use static (fixed) IP Addresses for Ethernet and Wi-Fi devices. Fixing the IP Address of the local computer connected to the router by a cabled Ethernet Local Area Network (LAN) connection is illustrated and explained first.
Some of the information is vague, such as “Now you can open the command prompt and do an ipconfig to see the network adapter settings have been successfully changed.” That means opening a Command Prompt, in all versions of Windows, and entering the command ipconfig at the end of the prompt. Press the Windows key plus the R key to bring up the Run box in any version of Windows and enter the cmd command to bring the Command Prompt window up. The command ipconfig /? provides all of the switches that can be used with the ipconfig command as shown in the image below.
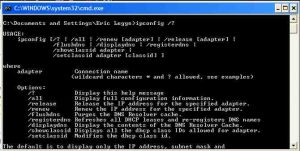
Networking Command Line [Command Prompt} Tools –
The network information, including the IP Addresses used by the router and the local computer, is provided. The router is called the Default Gateway. The other IP Address supplied will be the one given to the local computer that is being used to set its IP Address.
How to Assign a Static IP Address in Windows 7, 8, 10, XP, or Vista –
http://www.howtogeek.com/howto/19249/how-to-assign-a-static-ip-address-in-xp-vista-or-windows-7/
It is possible to run into a device-driver problem with a network interface card (NIC). The following problem was solved by the person who posted it just by updating the device driver for the network adapter on the PC that was not connecting to the network.
How To Fix All The Possible IP Address Errors? –
https://www.trickyenough.com/fix-ip-address-errors/
NEXT PAGE – Using a HomeGroup instead of a workgroup – A wireless guest network – Port forwarding